Are you aware of the Project Life Cycle and Stages in Oil & Gas Projects?
Project Life Cycle Phases& Stages in Oil & Gas Projects
The oil and gas industry is a major sector of the economy in the Gulf and different parts of the world. Oil and gas projects are usually capital-intensive, long-term, and potentially very lucrative. The revenues they generate are significant for both private companies and governments.
Project Life Cycle
A project life cycle specifies the sequence of stages that a project involves from its initiation to its closure.
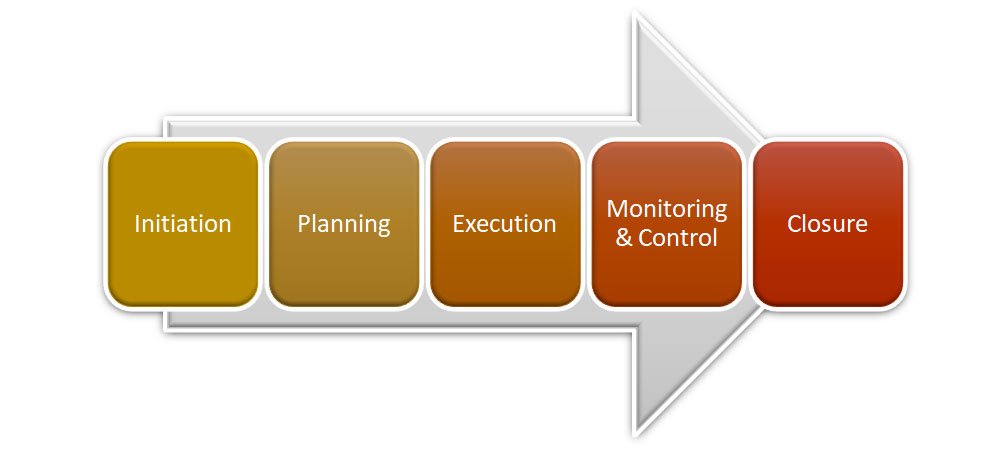
Initiation
- Collect Project Information
- Obtain Organizational Commitment
- Develop the Team
Planning
- Establish Project Objectives and SOW
- Plan the Work
- Plan and Estimate the Time for each work
- Plan the resources required
- Plan the cost budget
- Evaluate and create the baseline
Executing
- Distribute information
- Track work in progress and actual costs
Controlling
- Analyze and evaluate the project
- Recommend necessary action
- Update the project with realistic data
- Reforecast the schedule
- Communicate project performance to project team
Closing
- Document lessons learned
- Deliver the project to client or stakeholders
Project Stages
The Oil & Gas projects are broadly classified into 8 stages. The following are the stages that is involved in Oil & Gas projects:
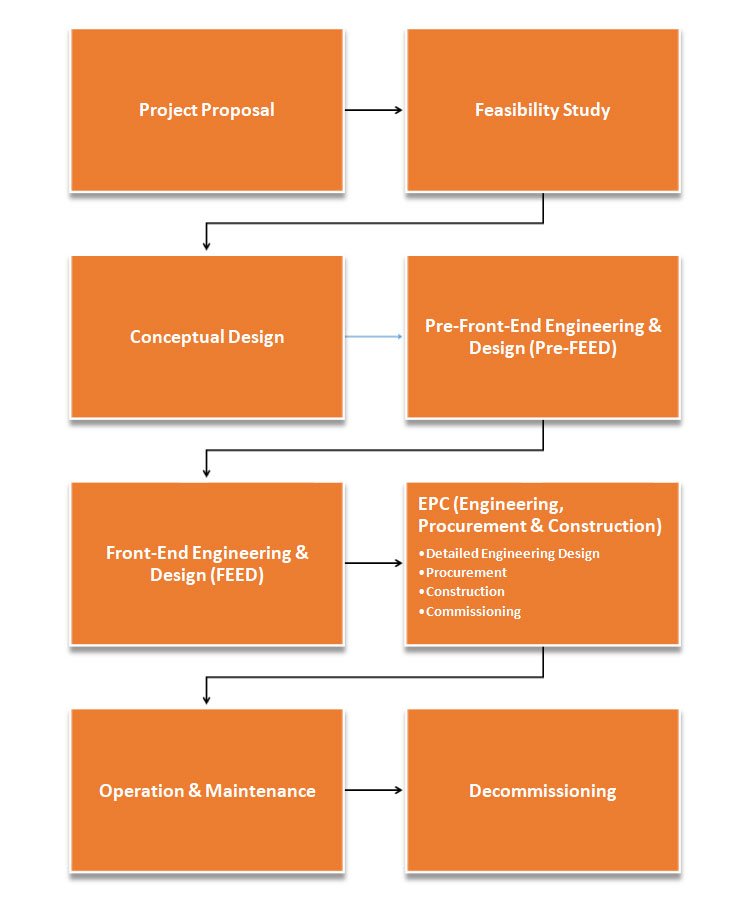
- Project Proposal: The project proposal outlines the scope, objectives, cost and the timeframe of the project.
- Feasibility Study: Feasibility Study is a study conducted to determine whether the project is viable. The types of feasibility include:
- Economic Feasibility
- Technical Feasibility
- Legal Feasibility
- Environmental Feasibility
- Conceptual Design: The conceptual design is the initial stage of design where the project’s basic structure and functionality are established. This includes selection of the appropriate technology, equipment and materials.
- Pre-Front-End Engineering & Design (Pre-FEED): Pre-FEED develops the foundation of project design and creates a set of boundaries to constrain and define the concept. The basis of project design outlines the operating characteristics of the project.The economic and technical feasibility of the basis of project design will be determined during Pre-FEED. The fund allocation is calculated for proceeding with engineering and design. Project boundaries are developed to deal with rules and regulations of the locality.
- Front-End Engineering & Design (FEED): FEED is defined as the work required to produce process and engineering documentation of sufficient depth to adequately define the requirements for detailed EPC ( Engineering, Procurement & Construction ) of facilities. The FEED is conducted after the completion of concept and feasibility studies where all the possibilities will be assessed from the perspective of technical, economic and safety.
- EPC (Engineering, Procurement & Construction)
- Detailed Engineering Design: The Detailed Engineering Design includes the development of detailed engineering drawings, specifications and calculations.
- Procurement – The procurement stage involves the identification of the suppliers, tendering and contract negotiation, purchase of materials, equipment and services that are required for the project.
- Construction: Construction stage involves he actual construction of the project. This involves Civil, Structural, Mechanical Piping and Equipment, Electrical, Instrumentation, Telecom, Pipelines & HSE.
- Commissioning: The commissioning stage is the final stage of the project, where in it is verified whether the facility has been designed, procured, fabricated, installed, tested, and prepared for operation or production as per the blueprint, design drawings, and specifications provided by the client. The facility is tested (Includes testing of equipment, systems and processes) and the systems are integrated and commissioned.
- Operation & Maintenance: After commissioning the project, the operation and maintenance of the facility starts which includes the monitoring of equipment, systems and processes as well.
- Decommissioning: As soon as the facility’s life gets over, the decommissioning is done which involves the safe and orderly dismantling and removal of the facilities.
The process of streamlining gets easier for the project managers and construction leaders when the stages of the project life cycle becomes easier to understand. From project initiation to closure, the organizations have the opportunity to develop quality timelines and establish clear project scopes to meet deadlines easily. The stakeholders, project team, contractors, suppliers and the regulatory bodies are involved throughout the entire project life cycle.
Created by: Navaneeth E P

